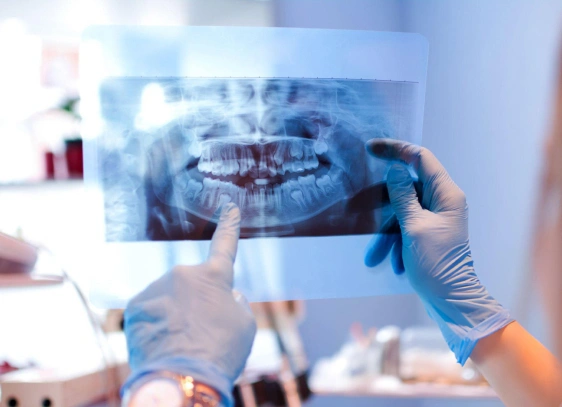
Benefits of Digital X-Rays
Dental X-rays, also known as dental radiographs, are essential tools for diagnosing issues in pediatric dentistry. They help dentists identify and treat problems like cavities, tooth decay, misalignment, bone injuries, and diseases early on. Many of these issues would be difficult to detect without X-rays.
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) recommends the use of dental X-rays for diagnosing conditions in children and teenagers. While these X-rays emit minimal radiation and are safe when used sparingly, AAPD guidelines aim to reduce unnecessary exposure to protect young patients.
What are dental X-rays used for?
- Evaluating the available space for incoming teeth.
- Ensuring primary teeth are shedding on schedule for adult teeth to come in.
- Monitoring the advancement of bone disease.
- Diagnosing and keeping track of tooth decay.
- Developing treatment plans, including orthodontic treatments.
- Identifying bone fractures, abscesses, and tumors.
- Detecting impacted wisdom teeth.
When will my child need dental X-rays?
The frequency of dental X-rays for a child will vary based on their individual circumstances. Children who are at a higher risk of tooth decay, as determined by their pediatric dentist, may need X-rays every six months to keep track of any changes. Similarly, children who are at a higher risk for orthodontic issues, such as malocclusion, may require more frequent X-rays for ongoing evaluation.
For children who are at an average or lower risk for decay and orthodontic problems, X-rays are usually taken every one to two years. Even if there are no immediate concerns about decay, regular X-rays are important to monitor the development of teeth and jaws and ensure there is enough space for permanent teeth to come in.
In cases of trauma or injury to the mouth, the pediatric dentist may recommend immediate X-rays. With advancements in X-ray technology, targeted imaging can be used to minimize unnecessary exposure while focusing on specific areas of the mouth.

